Accurate and reliable l land use/land cover (LULC) data are typically utilized as a crucial basis for research on resource management and ecological and environmental evaluation. Land resource surveys and remote sensing are main methods for understanding and grasping LULC changes. However, current LULC products lack updates and do not have sufficient access to finer-scale land survey statistics. To address these problems, Associate Professor Yu Le’s Research Group of the Department of Earth System Science (DESS), Tsinghua University has developed a practical and effective framework to automatically update and optimize existing LULC products (Fig. 1). Employing change detection algorithms, sample migration, and machine learning, this study has developed a framework for updating existing LULC products. Based on the data from the second national land survey (SNLS) and the third national land survey (TNLS), the study has further developed a statistical data spatial allocation method based on the minimum cross-entropy strategy to improve the consistency between the results of remote sensing monitoring and the statistical data of the SNLS and the TNLS.
The above research results have been published in International Journal of Digital Earth in the form of a paper titled “Integrating remote sensing temporal trajectory and survey statistics to update land use/land cover maps”.
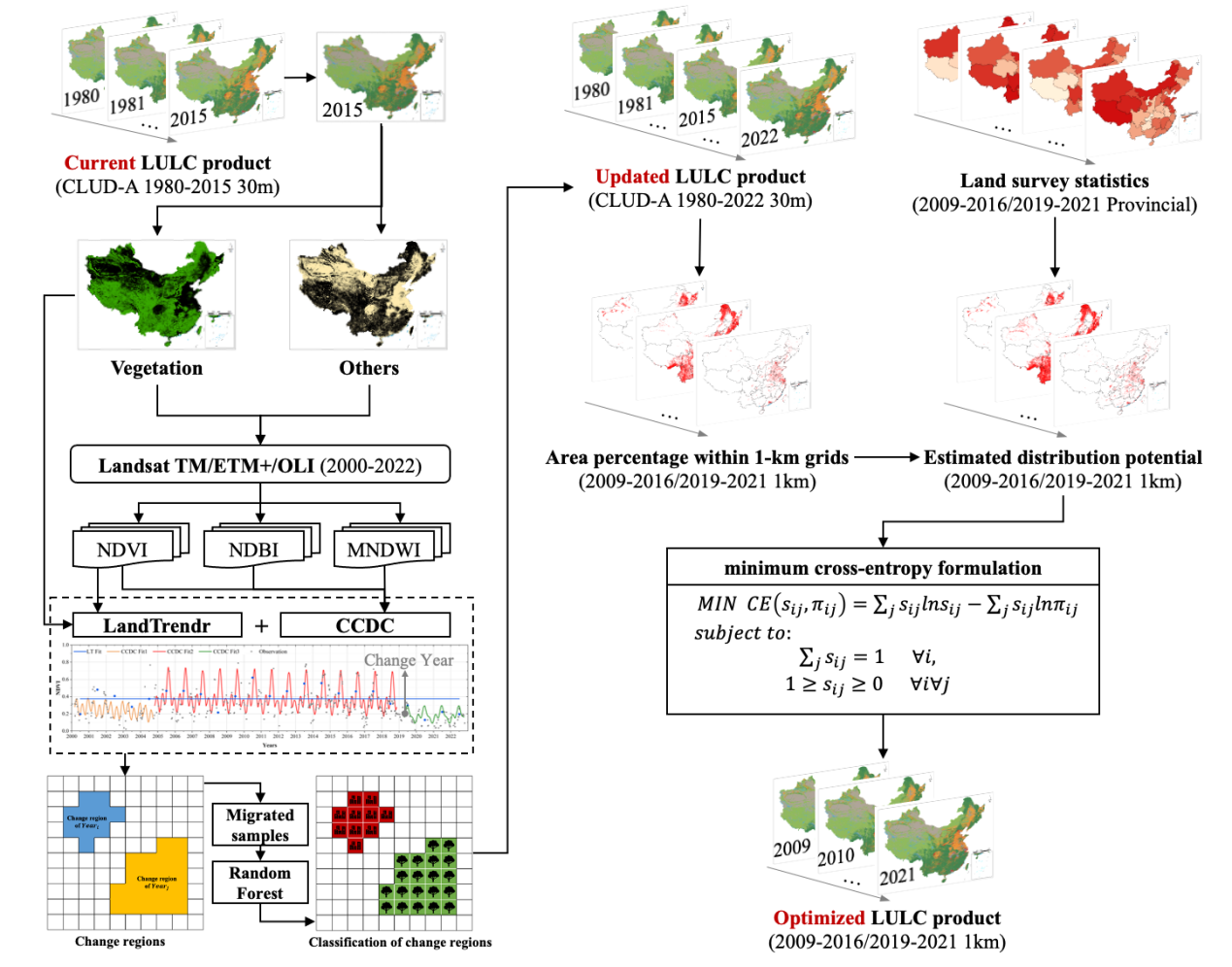
Figure 1. Workflow of the LULC product update using LandTrendr and CCDC, and optimization using the statistics space allocation method
The conclusion of the study shows that the updated maps demonstrate smooth continuity compared to the original dataset, and no unreasonable changes, without unreasonable changes in different LULC classification areas. Additionally, this method significantly improved the consistency between the LULC classification maps and land survey statistics (SNLS and TNLS) (see Fig. 2), can provide efficient and pragmatic solutions for upgrading current LULC remote sensing products, and has vital implications for continuous LULC change monitoring and sustainable management of land resources.
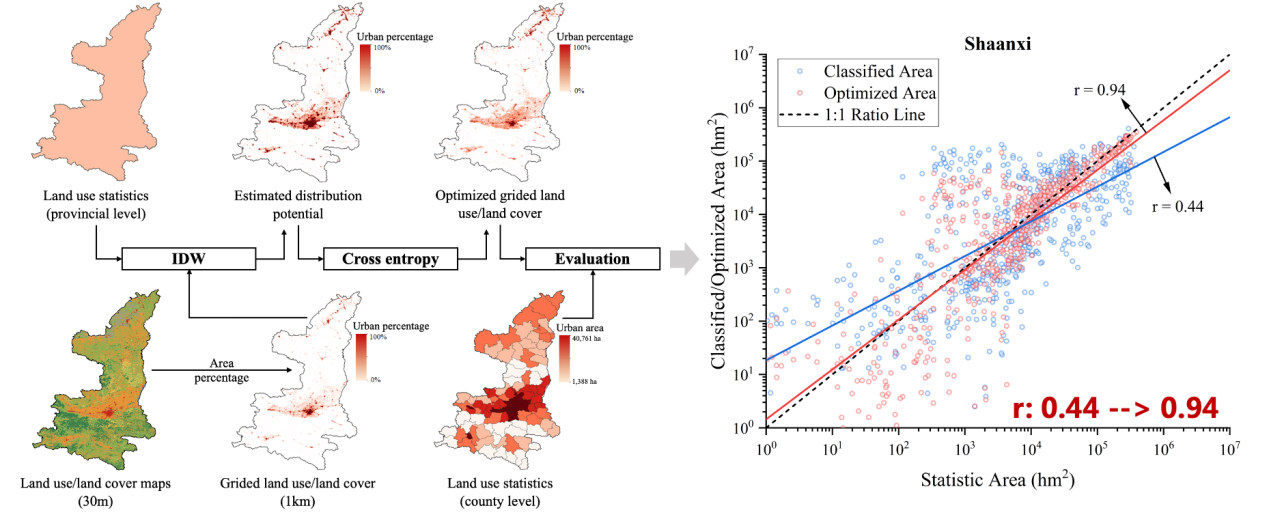
Figure 2. The workflow of land use/land cover (LULC) map optimization using the statistics space allocation method with Shaanxi Province as an example.
Doctoral fellow Du Zhenrong of the DESS, Tsinghua University (currently Associate Professor of the School of Information and Communication Engineering, Dalian University of Technology) is the first author of the paper. Co-authors include researchers from Tsinghua University, China Institute of Geo-Environmental Monitoring, Shanxi University, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the University of Hong Kong. This work was supported by Fundamental National Key R&D Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program.
Full-text link: https://doi.org/10.1080/17538947.2023.2274422
Written by Du Zhenrong
Edited by Wang Jiayin
Reviewed by Yu Le and Zhang Qiang