Recently, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has officially released the international standard ISO 19130-3, the first ISO standard established under the leadership of Tsinghua University in the field of geographic information.
Researcher Bai Yuqi at the Department of Earth System Science (DESS) presided over the formulation of the ISO standard, “ISO/TS 19130-3:2022 Geographic information--Imagery sensor models for geopositioning--Part 3: Implementation schema”. Experts from China, the United States, Canada, Germany and France spent two and a half years developing this standard. Jin Meng, a class 2017 doctoral student of the Department of Earth System Science participated in the whole course of the development of this standard.
Over a long period of time, no standard coding scheme was available for the sensor model used in the geopositioning of remote sensing images. Therefore, various data centers only provided remote sensing images, but could not provide the parameters of their geopositioning process. Although remote sensing data users could get the spatial position of image pixels, they were unable to understand their positioning process, and thus it was difficult for them to judge their positioning accuracy and evaluate the positioning accuracy of quantitative remote sensing data products. The coding scheme of sensor model offers an important method to address this problem.
However, there are obvious differences between the models of geopositioning process proposed by ISO and Open Geospatial Information Consortium (OGC). ISO 19130-1 and ISO 19130-2 have given the concept definition of geopositioning model, but no coding scheme is available. On the other hand, OGC has set a series of standards such as Earth observation sensor network from the perspective of geographic information service, but the description of the specific imaging methods and process itself is lacking. The research group analyzed and compared the existing models from such aspects as abstraction degree, object definition and attribute setting, put forward the method of model disassembly and mapping, realized a concrete scheme of semantic and syntax integration, and defined a detailed coding scheme of 84 classes and 377 parameters, covering seven kinds of passive and active observation situations, such as optics, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), laser radar (lidar) and sonar. The scheme is suitable for 90% of the 619 types of earth satellite observation sensors counted by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), and it is also suitable for most aerial sensors.
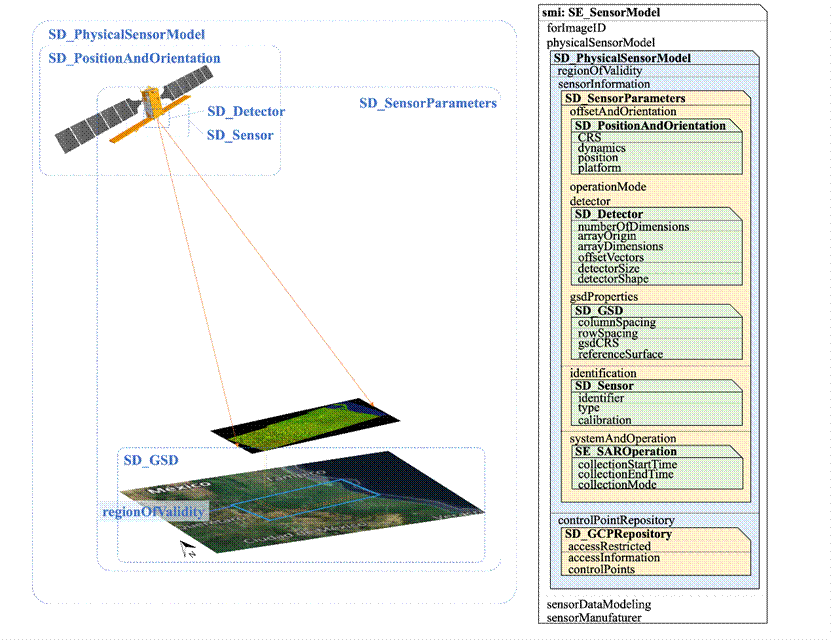
The research group further advanced the development of a standard for the research results in the ISO Geographic Information Technology Committee (TC 211), consulted more than 2,500 pages of relevant ISO and OGC standard texts, ensured that the standard texts and reference appendices be scientific, systematic and accurate, and finally completed the formulation of the ISO 19130-3 standard. The ISO 19130-3 standard solves the long-standing problem of the absence of a coding scheme for remote sensing image geopositioning models, and is helpful for accurate and rapid fusion of multi-source remote sensing data and reliability test of geopositioning information. This standard enhances the modularization and standardization of remote sensing image geopositioning information processing, and improves the compatibility and robustness of remote sensing ground system software. This achievement also provides technical support for the research of "trusted remote sensing" and "trusted interoperability of earth observation".
During the period of presiding over the development of this international standard, Researcher Bai Yuqi was unanimously elected as the convener of the ISO/TC 211 Information Community Working Group in January 2020 through national recommendation, competitive selection, committee interview and voting of member countries, becoming the first Chinese expert to serve as a convener of a working group since China joined ISO/TC 211 in 1994.
ISO is an independent, non-governmental international organization with a membership of 167 national standards bodies (including countries and regions). The strategic goal of ISO is to bring together experts to share knowledge and develop voluntary and consensus-based International Standards that support innovation and provide solutions to global challenges. ISO/TC 211 established in 1994 is concerned with the standardization in the field of digital geographic information.
Contributed by Bai Yuqi and Jin Meng
Edited by Wang Jiayin
Reviewed by Zhang Qiang