Recently, CESS Ph.D candidate Lv Baolei published a paper online as the first author called” Improving the Accuracy of Daily PM2.5 Distributions Derived from the Fusion of Ground-Level Measurements with Aerosol Optical Depth Observations, a Case Study in North China” on the journal of Environmental Science & Technology, which is a prestigious journal on environment science. And Associate Professor Bai Yuqi is the corresponding author. The co-authors include Yongtao Hu and Armistead Russell in Georgia Institute of Technology and Howard Chang in Emory University.
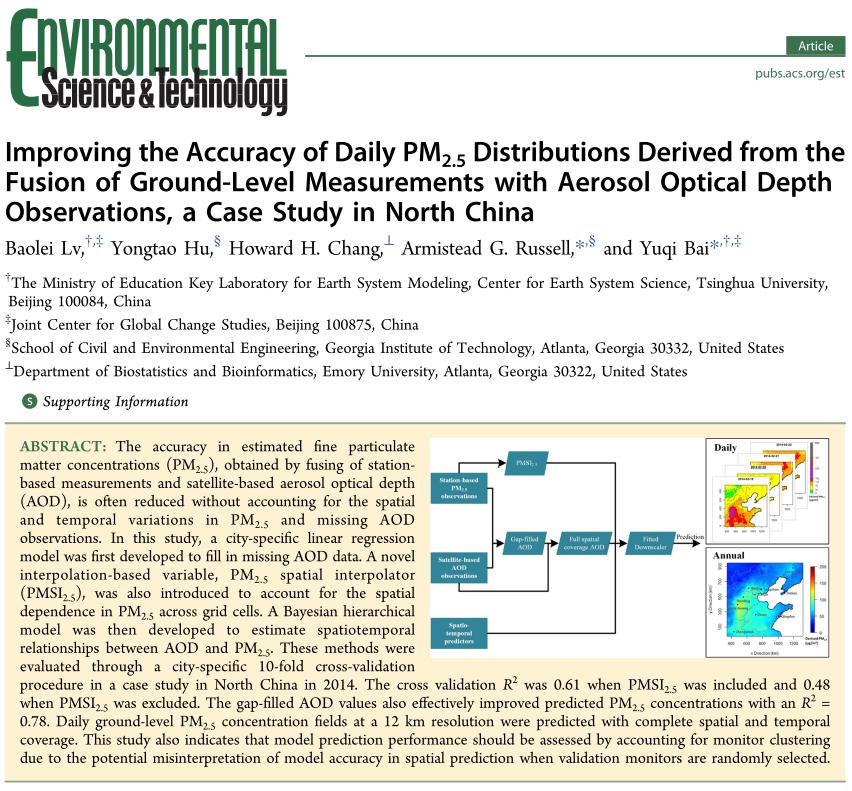
Figure 1 ES&T published this paper online
The accuracy in estimated fine particulate matter concentrations (PM2.5), obtained by fusing of station-based measurements and satellite-based aerosol optical depth (AOD), is often reduced without accounting for the spatial and temporal variations in PM2.5and missing AOD observations. In this study, a city-specific linear regression model was first developed to fill in missing AOD data. A novel interpolation-based variable, PM2.5spatial interpolator (PMSI2.5), was also introduced to account for the spatial dependence in PM2.5across grid cells. A Bayesian hierarchical model was then developed to estimate spatiotemporal relationships between AOD and PM2.5. These methods were evaluated through a city-specific 10-fold cross-validation procedure in a case study in North China in 2014. The cross validationR2was 0.61 when PMSI2.5was included and 0.48 when PMSI2.5was excluded. The gap-filled AOD values also effectively improved predicted PM2.5concentrations with anR2= 0.78. Daily ground-level PM2.5concentration fields at a 12 km resolution were predicted with complete spatial and temporal coverage. This study also indicates that model prediction performance should be assessed by accounting for monitor clustering due to the potential misinterpretation of model accuracy in spatial prediction when validation monitors are randomly selected.

Figure 2 Annual and seasonal mean estimations of the PM2.5 concentrations using the full model and reconstructed AOD data set.
Environmental Science & Technology is a top journal on environment science.According to Thomson Reuters Citation report in 2014, the impact factor ofRemote Sensing of Environmentis 5.33.
Paper link:
Lv, B., Hu, Y., Chang, H.H., Russell, A.G., Bai, Y. (2016) Improving the Accuracy of Daily PM2.5 Distributions Derived from the Fusion of Ground-Level Measurements with Aerosol Optical Depth Observations, a Case Study in North China. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05940
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.est.5b05940