Recently, CESS Ph.D. candidate Lv Baolei published review paper called “A systematic analysis of PM2.5 in Beijing and its sources from 2000 to 2012” on the journal of Atmospheric Environment as the first author. Associate Professor Bai Yuqi is the corresponding author, and alumnus Dr. Zhang Bin is a co-author of this paper. Associate Professor Wang Yuxuan also provided help in writing this paper.
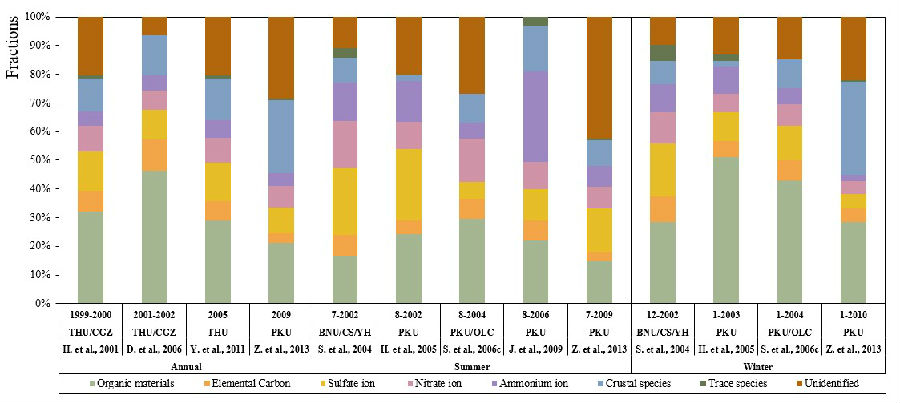
Figure 1 Observed variation of PM2.5 composition in Beijing from 2000 to 2012
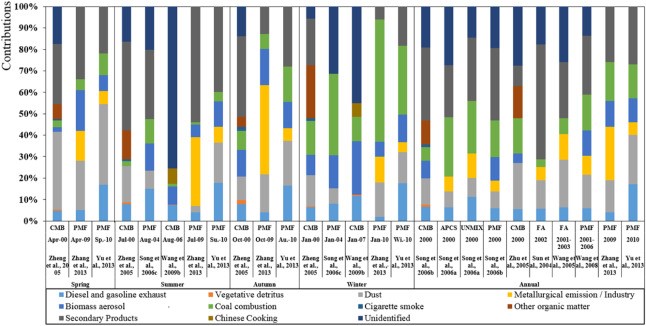
Figure 2 Source apportionment results in Beijing from 2000 to 2012
Since 2000, many groups have studies on measurement and analysis of PM2.5 in Beijing. Those results reflected the characteristics of PM2.5 pollutants in Beijing during different times. Yet the problem is a lack of a comprehensive analysis of long-term trend of PM2.5 in Beijing. This paper collected data of measurements in Beijing from over 60 studies that have been published in peer-reviewed journals. It mainly contains concentration, composition of PM2.5, as well as source apportionment results given by receptor models. Based on the dataset, the paper used non-parametric estimation method called “Theil-Sen” method to analyze the trend. The method could effectively avoid the impact of abnormal values on the evaluation of trend. This study showed long-term trends that seasonal variation of PM2.5 concentration is significantly decreasing, yet OC/EC concentration has not obviously changed, while mineral salt concentration rises in summer and drops in winter. This study is of great importance in acknowledgement of particulate matter change in the last decade in Beijing and evaluation of multiple emission reduction policies. Reviewer said “This paper may be of high interest for the scientific community because of its valiant attempt to resume sparse data and studies. Its publication is then strongly recommended in AE journal.”
Lv, B., Zhang, B., & Bai, Y. (2015). A systematic analysis of PM2.5 in Beijing and its sources from 2000 to 2012. Atmospheric Environment.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1352231015303733